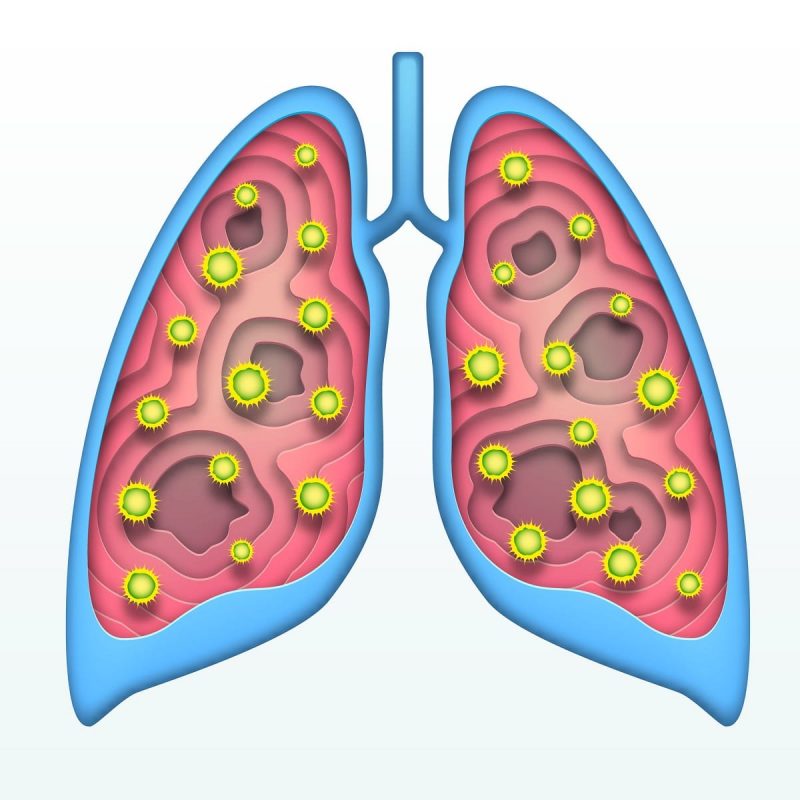
Tuberculosis (TB)
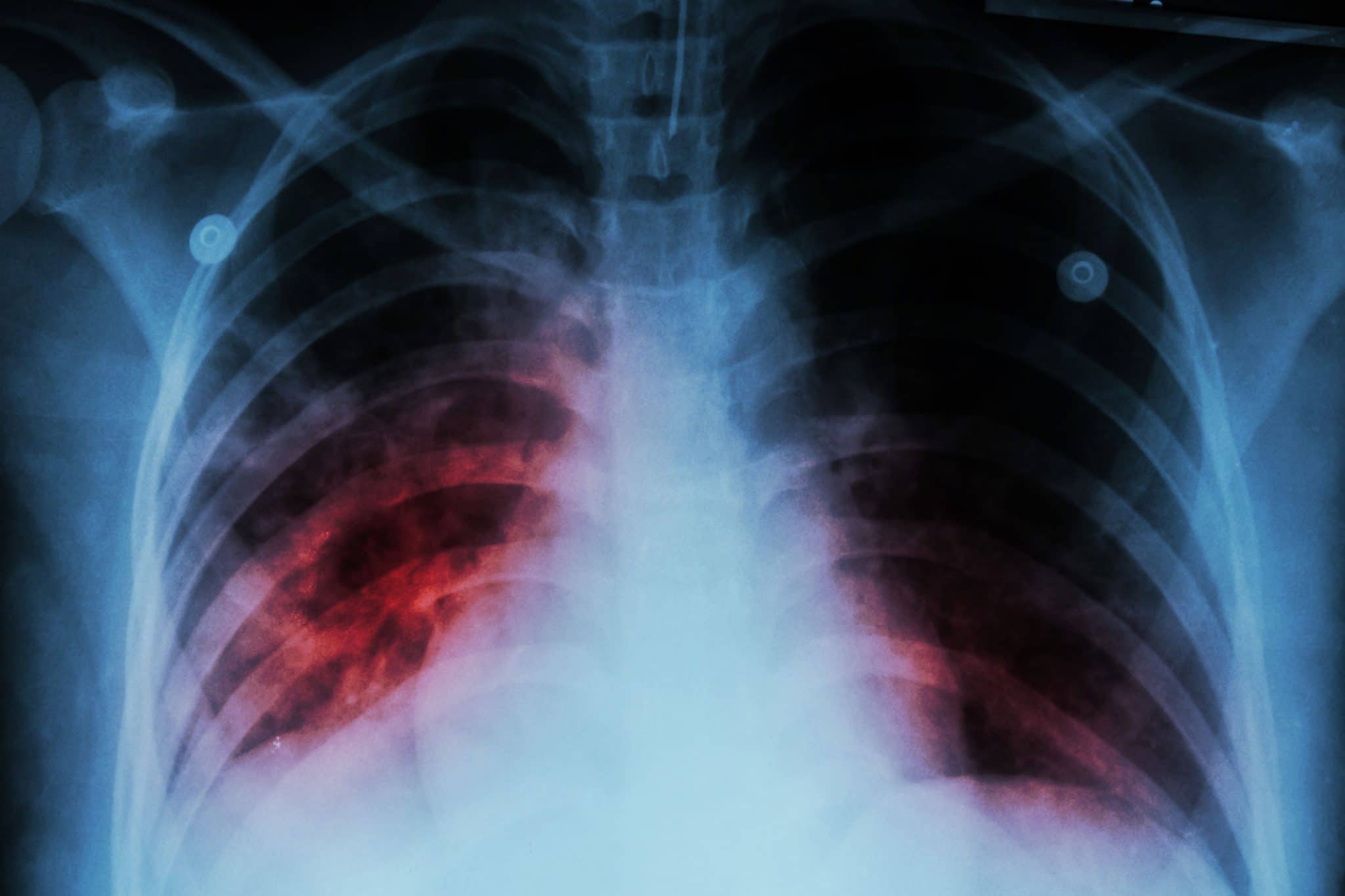
RISK FACTORS [2]
- Immunocompromised persons: especially those infected with HIV.
- Living or being around someone who has TB.
- Very young or advanced age.
- Someone who has recently been affected with the TB bacteria.
CAUSES [2]
It spreads through air droplets when someone with lung TB coughs, sneezes or spits and the microbes propels in the air. Someone then needs to inhale these microbes to become infected with the disease.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS [2]
- Cough for more than two weeks.
- Night sweats: wake up at night and must change your clothes.
- Unintentional weight loss: cannot fit into clothes.
- Fever.
- Loss of appetite.Fatigue.
- Can experience chest pain or pain while breathing
COMPLICATIONS [2]
- Pain in the spine.
- Damage to your joints, especially the hip and knee joints.
- Meningitis.
- Problems with your liver or kidney.
- Heart disorders.
- Coughing up blood.
- Malignancy.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES [3]
- Stay at home until the doctor says that you can return to your normal activities.
- The people that stay with you must also see a doctor to check if they have active TB.
- Make sure you take the proper therapy as directed by the doctor.
- Do not miss any medications. Remind yourself with a calendar, an alarm on your phone or ask a friend or family member to remind you.
- Talk to your doctor about directly observed therapy.
- Keep your house well aired.
- Eat a healthy diet.
Related Brochures

hiv-11-hiv-and-opportunistic-infections
Doctors were first alerted to the existence of AIDS when patients clinically presented with opportunistic ....