Varicella Vaccine
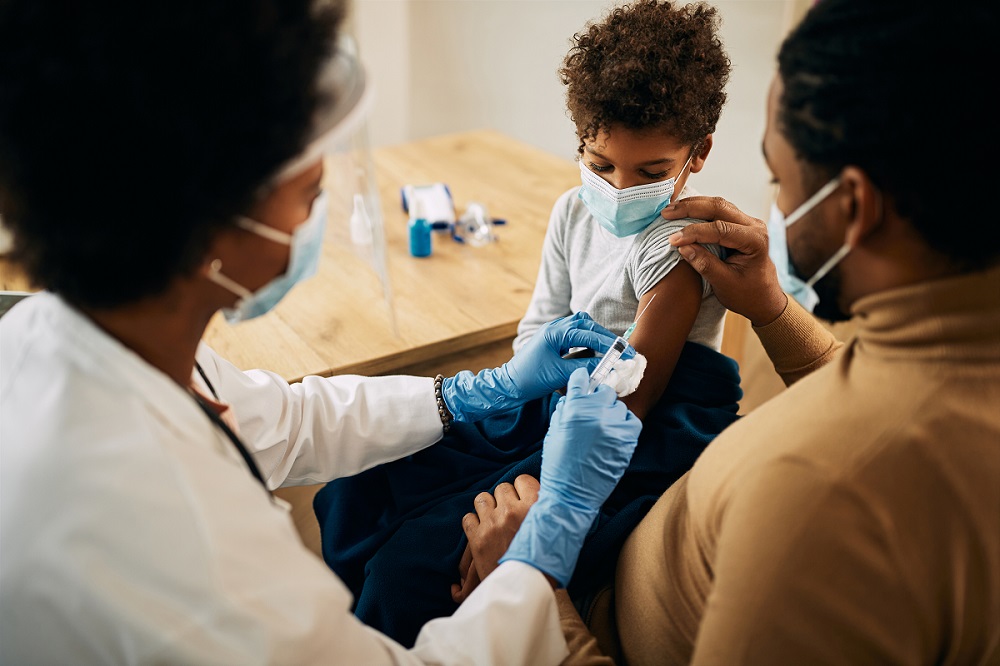
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is characterized by an itchy rash, fever, and general discomfort. Chickenpox primarily affects children but can also occur in adults, often with more severe symptoms. Fortunately, the varicella vaccine is a safe and effective way to prevent chickenpox and its complications.
What is Chickenpox?
Chickenpox is known for causing an itchy rash that typically begins as small red spots that develop into fluid-filled blisters. Other common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
While chickenpox is usually mild in children, it can lead to serious complications, such as bacterial infections of the skin, pneumonia, and inflammation of the brain (encephalitis).
How Does the Varicella Vaccine Work?
The varicella vaccine contains a weakened form of the varicella-zoster virus. When administered, it stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the virus. This means that if a vaccinated person is later exposed to chickenpox, their immune system will be ready to fight off the infection, significantly reducing the chances of getting sick.
Vaccination Schedule
In South Africa, the varicella vaccine is part of the Expanded Programme on Immunisation (EPI). The vaccine is typically given as follows:
- The first dose is administered to children at 12 months of age.
- A second dose is given between the ages of 4 and 6 years.
It’s important to follow this vaccination schedule to ensure that your child is adequately protected against chickenpox.
Why is the Varicella Vaccine Important?
- Prevents Chickenpox: The vaccine is highly effective at preventing chickenpox, which means fewer children will suffer from the illness and its associated complications.
- Reduces Severity: In cases where vaccinated individuals do contract chickenpox, the symptoms are often milder and shorter in duration compared to unvaccinated individuals.
- Community Health: High vaccination rates contribute to herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with certain medical conditions.
Is the Varicella Vaccine Safe?
Yes, the varicella vaccine is considered safe and effective. Most children experience only mild side effects, including:
- Soreness or redness at the injection site
- Mild fever
- A few spots resembling chickenpox (this is normal and usually resolves quickly)
Serious side effects are rare, and the benefits of vaccination far outweigh any potential risks.
Common Misconceptions
Some people may believe that chickenpox is just a mild illness and that vaccination is unnecessary. However, chickenpox can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations.
Others may worry that getting the vaccine will cause chickenpox. While the vaccine can cause a few mild spots, these are usually much less severe than the actual disease.